FDA Publishes 2021 Report on Antimicrobial Use in Livestock
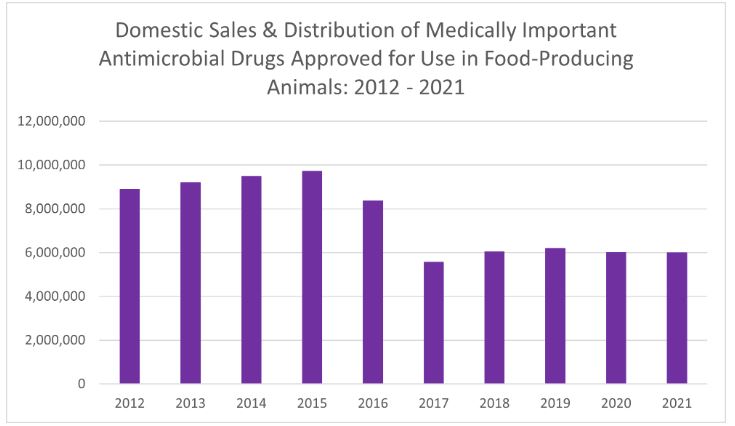
Domestic sales and distribution of medically important antimicrobial drugs approved for use in food-producing animals decreased by less than 1% between 2020 and 2021. Since the significant decrease in sales volume in 2017, annual sales of medically important antimicrobials have remained at reduced levels, according to the U.S. FDA's Center for Veterinary Medicine's (CVM) 2021 Summary Report on Antimicrobials Sold or Distributed for Use in Food-Producing Animals. Compared to 2015 (peak year of sales), 2021 sales decreased 38%.
FDA notes that fluctuations in sales volume can occur over time in response to various factors such as changing animal health needs or changes in animal populations. Given the substantial change that occurred with transitioning a large number of products containing medically important antimicrobials from over-the-counter use to a marketing status requiring veterinary oversight at the beginning of 2017, some rebound in the reported sales volume in subsequent years was not unexpected as affected stakeholders adjusted to the new requirements, FDA said in its report.
Source: FDA
"While sales data on antimicrobial drug products intended for food-producing animals do not necessarily reflect the actual use of antimicrobial drugs, sales volume observed over time can be a valuable indicator of market trends related to these products," the report said. "However, when evaluating the progress of ongoing efforts to support judicious use of antimicrobials, it is important to take into account additional information sources including actual use data, animal demographics, animal health data, and data on antimicrobial resistance."
The domestic sales and distribution of medically important antimicrobials approved for use in food-producing animals for 2021 included:
- An estimated 41% was intended for use in cattle, an estimated 42% intended for use in swine, an estimated 11% intended for use in turkeys, an estimated 3% intended for use in chickens, and an estimated 3% intended for use in other species/unknown.
- Tetracyclines accounted for 65%, penicillins for 10%, macrolides for 9%, sulfonamides for 5%, aminoglycosides for 6%, lincosamides for 3%, cephalosporins for less than 1%, and fluoroquinolones for less than 1%.
- An estimated 79% of cephalosporins, 45% of sulfonamides, 52% of aminoglycocides, and 43% of tetracyclines were intended for use in cattle. An estimated 89% of lincosamides and 41% of macrolides were intended for use in swine. An estimated 72% of penicillins were intended for use in turkeys.
Slowing the development of antimicrobial resistance helps preserve the effectiveness of antimicrobials for fighting disease in animals and humans, FDA explained. The agency's aim is not solely measured by reduced sales volume of antimicrobials, but also includes placing these products under veterinary oversight, fostering good antimicrobial stewardship practices by optimizing the use of these products, and limiting their use to only when necessary to treat, control, or prevent disease.
The three overarching goals in the plan are:
Goal 1: Align antimicrobial drug product use with the principles of antimicrobial stewardship
- Veterinary Oversight of Medically Important Antimicrobial Drugs
- Duration of Use of Medically Important Antimicrobial Drugs
- Enhancing Processes to Support New Product Development
Goal 2: Foster stewardship of antimicrobials in veterinary settings
- Education and Outreach
- Veterinary Feed Directive
Goal 3: Enhance monitoring of antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial drug use in animals
- Antimicrobial Use in Animals
- Antimicrobial Resistance in Animals