Feeding High-Magnesium Minerals to Cows Calving on Winter Pastures

There has not been much wheat pasture this winter after a slow start last fall and long winter drought in most of Oklahoma. Many pastures that usually have stockers grazing all winter had either not been stocked or have had the calves pulled already. Moisture from last week’s snow will give the wheat a boost and many of these fields could be used for spring calving cows to graze. Growing wheat this time of year is high in protein and highly digestible and will easily meet the requirements of a beef cow in early lactation.
A problem with wheat and other small grain pasture is the mineral content in comparison to the needs of the lactating cow. The following table shows the average mineral content from 5 experiments across Oklahoma and into Arkansas.
There is considerable variation in the mineral composition of small grain forages, depending on management, growth conditions, and soil mineral content. This data shows that magnesium, copper and zinc are deficient in wheat forage; calcium and phosphorus are adequate while potassium is excessive.
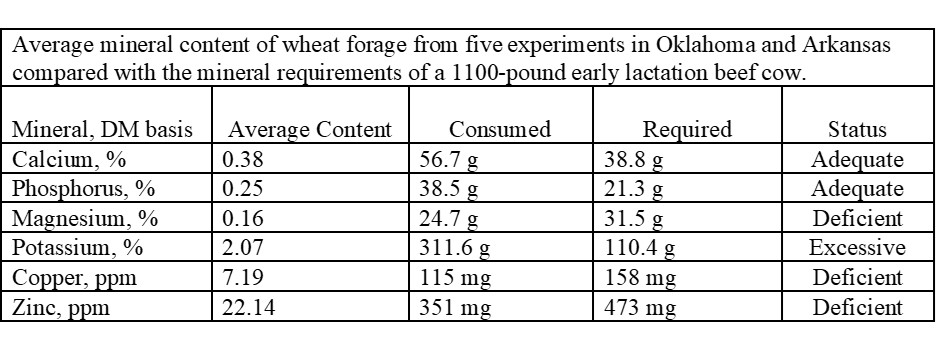
Average mineral content of wheat forage from five experiments in Oklahoma and Arkansas compared with the mineral requirements of a 1100-pound early lactation beef cow.
The high potassium content of wheat forage is problematic because it interferes with magnesium absorption in the gastro-intestinal tract. Grass tetany in mature cows is caused by low blood magnesium levels that can result from either low magnesium intake or poor absorption. It is commonly a problem in nursing mature cows grazing small grain pastures in the spring due to magnesium excretion in the milk and reduced resorption of magnesium from the bone in mature cows compared with younger cows or growing calves.
Grass tetany is a condition associated with inadequate magnesium in the diet. Magnesium is a mineral that is necessary in nerve function and therefore muscle contraction. Cattle with grass tetany become excitable, develop muscle tremors, and have difficulty breathing and in the worst case, death.
The most common method of preventing grass tetany is to supplement the herd with magnesium beginning at least 1 month prior to spring grazing. Mineral supplements that contain 10 to 12% magnesium as magnesium oxide, called High Mag minerals in lay terms, are commonly used. At 3 to 4 oz intake, such minerals will provide 40 to 50% of a cow’s daily magnesium requirement. Mineral supplement intake is often reduced when higher rates of magnesium are added due to the unpalatability of magnesium oxide. Mineral mixtures will not effectively offset mineral deficiencies if desired amounts are not consumed, therefore intake must be monitored.







