Where Diagnosis and Parole Boards Meet

This article was developed by Meredyth Jones, DVM, MS, DACVIM. She is an associate professor of food animal medicine and surgery at Oklahoma State University and owns Large Animal Consulting & Education.
You open the trailer door, and there he stands: a 500-lb. steer breathing hard, mouth wide open with strings of saliva hanging down. When you get him into the chute his temperature is 104.1°F, and his lungs sound raspy. What is your diagnosis?
If you are consistent with your physician colleagues, you will generate a differential diagnosis list for this case in as quickly as 28 seconds and arrive at your final diagnosis in 1 to 7 minutes [Kuhn 2002].
We are lightning fast at this because our minds are wired for pattern recognition and practical approaches to problem-solving that achieve the short-term goal but aren’t always optimal.
We use bits and pieces of information from the case to calculate the probability that a disease is present, as stated by Bayes’ Theorem of Clinical Diagnoses.
You see a young, growing steer breathing hard and with a fever, and that pattern tells you it’s most likely BRD. You also come up with the possibility that he’s choked, which may even lead you to think about rabies, so you’ll put some gloves on.
But did you consider that he might have a urinary obstruction? That’s what was wrong with this specific steer. This phenomenon is also why lame cows get treated at home for weeks with antibiotics for a home diagnosis of footrot, when they actually have a septic joint. It’s why cases of rabies get missed.
A lame cow with a swollen foot equals footrot, and a neurologic calf on a hot ration equals polio. Until they don’t.
Decision Fatigue and Ego Depletion
Every decision we make costs us something. As we move through our day, making decision after decision, our accommodation for being tired is to select the least-risk decision as we lose willpower (ego depletion). This has been demonstrated in other professions, including with judges and physicians.
In one study, judges reviewing parole requests were given two daily meal breaks [Danzinger et al, 2011]. The judges made significantly more unfavorable decisions toward the offender in the later part of each decision session compared to earlier in the session, right after they had eaten.
In physicians examining patients with acute respiratory infections [Linder et al 2014], the odds ratio for prescribing antimicrobials was greater later in the day relative to the start of the day.
If we have to decide whether to parole the bad guy and we are rested and feel capable of weighing all the factors, we might give him a chance. But late in the day when we are tired and don’t want to risk it, we deny parole.
Early in the day we might be able to resist the client requesting antibiotics for a case where they are not indicated, but late in the day we don’t quite trust ourselves and give the drug just in case.
Resource Limitations
Veterinarians function at a very high level in the face of time, information and client-finance limitations. We face dynamic and changing situations daily. The information about a case we receive from our clients is based on their interpretation of the signs and situation, subject to their inherent biases.
We perform our physical examination and develop a differential diagnosis list. Then, we might be faced with another information challenge: We don’t have needed diagnostic testing available, or we don’t have access to the study that tells us where to go from here.
The effect of time limitations can be two-fold: we simply do not have the time to devote to fully researching and solving a complex case, or the rush to work through a case could result in cognitive or decision errors. We also lose a lot of time to distractions.
Distractions can cause a loss of 40% of productivity, and it takes an average of 23 minutes [Mark et al, 2005] for our brains to get back on task when we’re interrupted.
Affect Influences
The patterns of our day, when we last ate and how much sleep we got, have obvious impacts on our mood and decision-making ability. Did you know in human medicine, it is known that a patient making a physician uncomfortable impairs decision-making and increases the risk of medical error?
For us, it might be a particular client who throws us so far off our game we are unable to give our full energy and attention to the case they present. Now, what are we going to do about this?
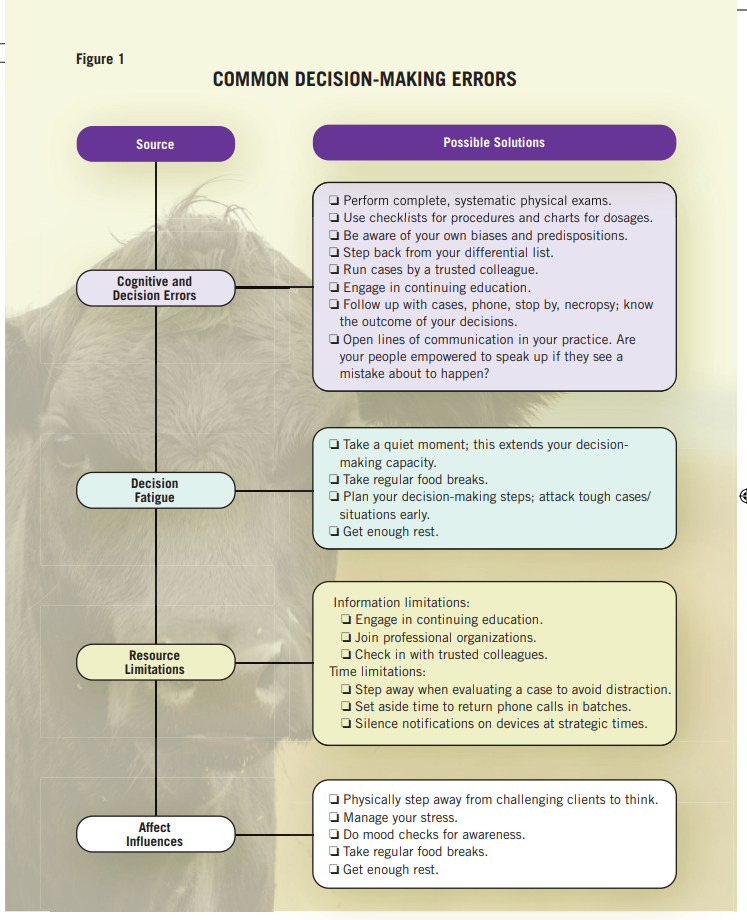
It has been said the act of diagnosis is the most difficult undertaking of human beings. Medical errors seem inevitable, but there are small steps we can take to address many of the contributing factors.
Consider your options (Figure 1) the next time you catch yourself forming an opinion or making a decision too quickly with too few facts in hand.







